How to develop an investment strategy


It's important to have a clear, precise investment objective. Your investment objective should consider factors such as the level of income or capital growth you're seeking to achieve, and for what purpose. You'll also need to consider your risk appetite, which is what level of risk you are willing to take, when developing an investment objective.
Consider what your investment timeframe is. If you have a long-term investment timeframe, you may have more capacity to ride out any market downturns or volatility, and so could consider investments with higher risk / higher return profiles (such as shares). If your investment timeframe is short, you may want to be more cautious.
Diversifying across asset classes could protect you against underperformance in any one asset class. Your asset allocation can reflect how cautious or aggressive your investment strategy is.
Determine how much of your portfolio you want in each of the asset classes (cash, fixed interest/bonds, property and shares). It's important to rebalance your portfolio throughout its life to ensure that your asset class weightings continue to be appropriate for you.
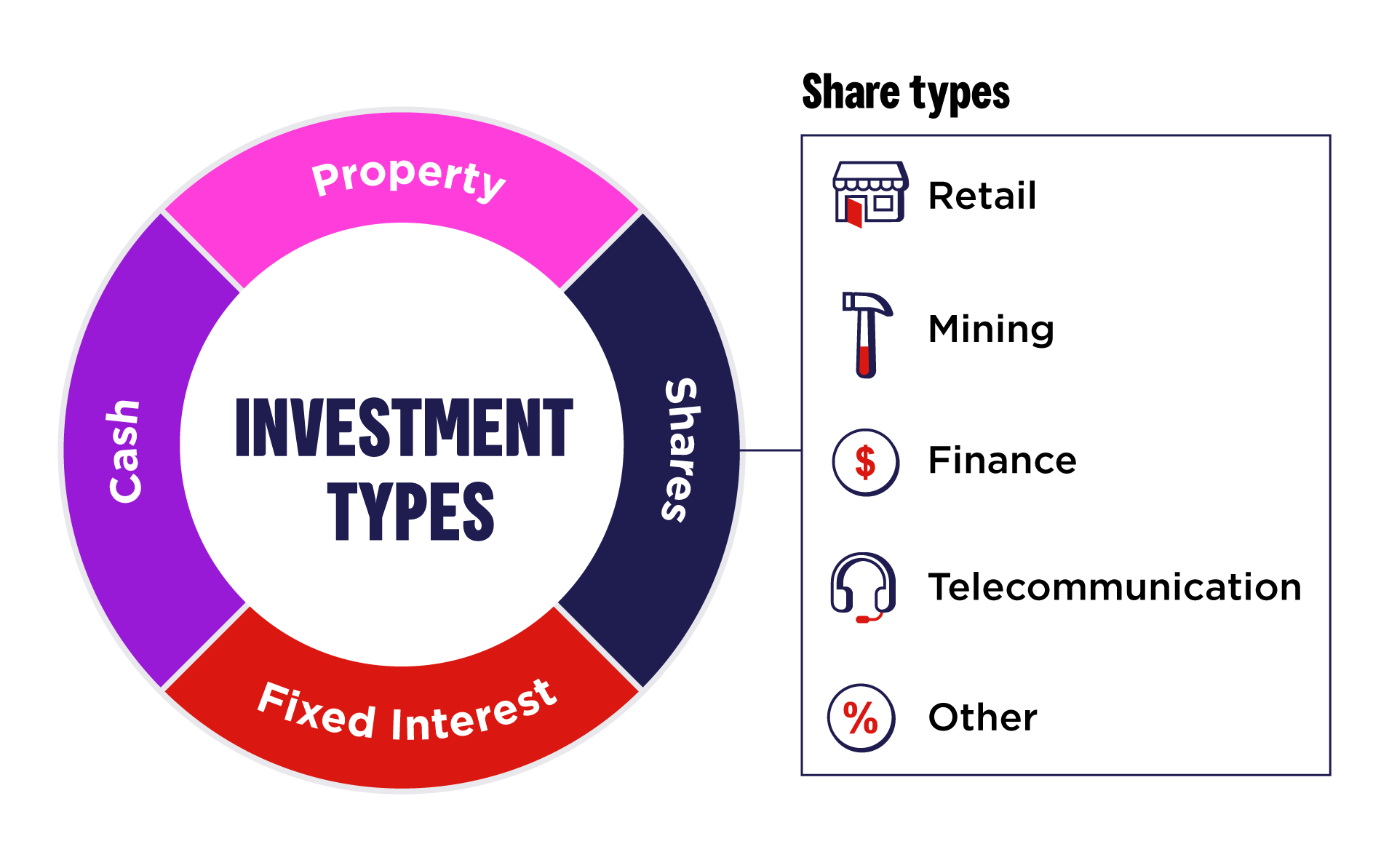
Determine the types of investments you are happy to make, and those that you won’t make. For example, will you invest in speculative mining stocks, stick to big, well-established blue-chip companies or a combination of both? You can revisit your investment objectives over time and adjust accordingly with your skill level and risk appetite.
Identify the risks to your investment strategy, and how you’ll mitigate and manage those risks. Risk management is one of the most important steps when establishing your investment strategy.
In this digital age we're blessed with access to a tremendous amount of information, research and tools that can help us to make investment decisions. If you don’t have the confidence to make investment decisions by yourself, you can seek professional assistance from a financial advisor.
The below are four types of common investing strategies through share trading for your consideration:
Passive investing can be a cost-effective, long-term strategy that involves buying and holding investments with little day-to-day trading. The goal is to mirror the performance of a specific market index or benchmark, rather than trying to outperform it. This approach aims to benefit from the market’s general upward trend over time while keeping trading fees and associated costs to a minimum.
Passive investing offers several potential advantages, including lower costs due to minimal trading and management fees, simplicity through easy-to-access passive funds or ETFs, and broad diversification across various sectors. It also provides the potential for long-term growth aligned with overall market performance, while giving investors the flexibility to adopt a straightforward buy-and-hold approach.
Growth investing is a strategy where investors target companies that are expected to outpace the market in terms of growth, with the goal of achieving capital gains. Growth investors look for businesses with strong potential for future earnings and revenue expansion.
Growth investing could lead to faster profits as stock prices of growth companies can rise quickly and at times exponentially. It is important that you understand any potential risks associated with this strategy such as valuation, volatility and market sentiment risks. These stocks may also not pay dividends as the company preferences overall capital growth.
Value investing finds stocks that seem to be priced lower than what they’re really worth based on the strength of the underlying business. It’s a longer-term approach, built on the idea that, over time, the market will catch on and the stock’s price will rise to reflect its true value.
Value investing offers the potential for strong long-term returns as stock prices catch up to a company's true worth as market sentiment changes. These types of investments often come with a strong risk/reward balance and are backed by fundamental analysis and key financial metrics.
Income investing focuses on generating regular income from your investments. This is typically done through dividends from shares, interest from bonds, or distributions from real estate investment trusts (REITs).
While growth investors are looking to increase the overall value of their portfolio over time, income investors prefer to prioritise stable, recurring cash flow from their investments.
The information on this website has been prepared without taking account of your objectives, financial situation or needs. Because of this, you should consider its appropriateness, having regard to your objectives, financial situation and needs and, if necessary, seek appropriate professional advice. If a Product Disclosure Statement is available in relation to a particular financial product, you should obtain and consider that Product Disclosure Statement before making any decisions about whether to acquire the financial product. The information contained on this website does not constitute the provision of advice or constitute or form part of any offer, solicitation or invitation to subscribe for or purchase any securities or other financial product nor shall it form part of it or form the basis of or be relied upon in connection with any contract or commitment whatsoever. Any securities or prices used in the examples on this website are for illustrative purposes only and should not be considered as a recommendation to buy, sell or hold. Past performance is not a reliable indicator of future performance. This website may contain material provided directly by third parties. This information is given in good faith and has been derived from sources believed to be accurate at its issue date. While such material is published with necessary permission, no company in the Westpac Group nor any of their related entities, employees or directors (together, "Westpac"), nor the Participant, accepts responsibility for the accuracy or completeness of, or endorses any such material. This website may also contain links to external websites. Westpac and the Participant do not accept responsibility for, or endorse the content of, such external websites. Except where contrary to law, Westpac and the Participant intend by this notice to exclude liability for material provided directly by third parties and the content of external websites.